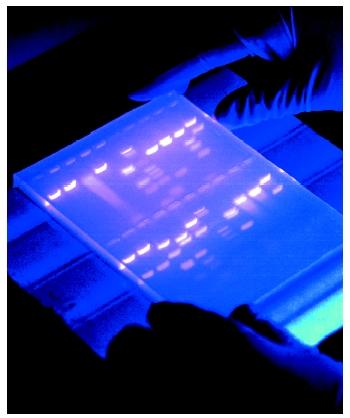
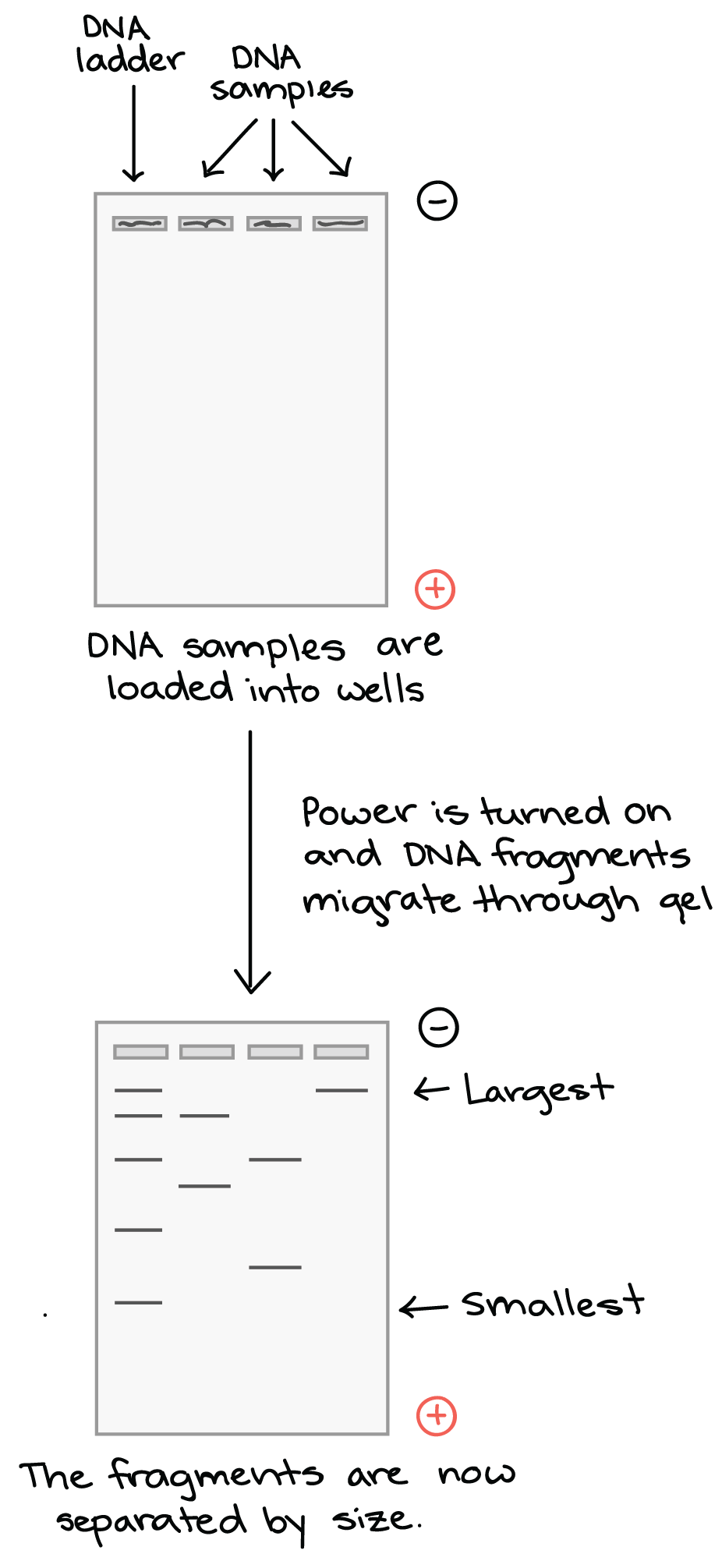
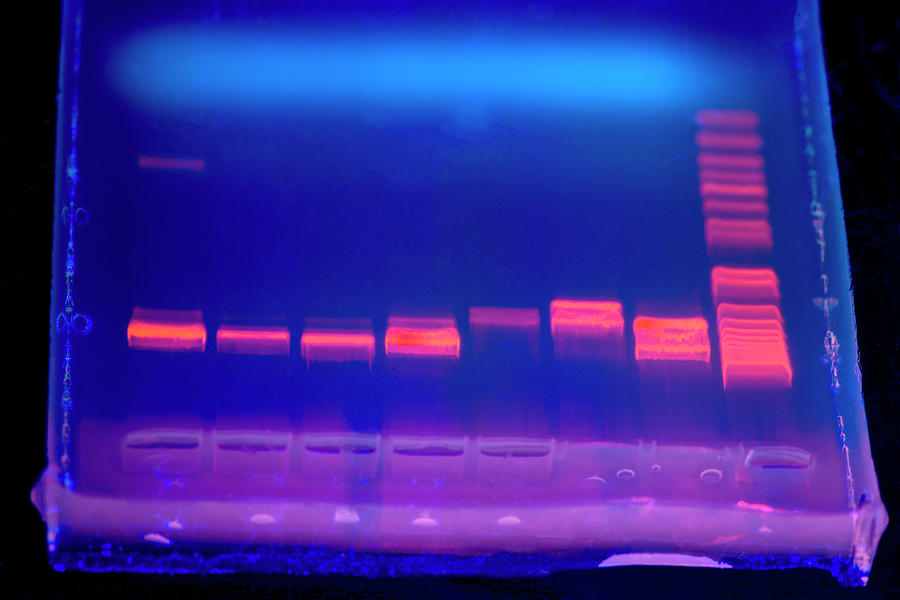
- Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments (or other macromolecules, such as RNA and proteins) based on their size and charge.
- A technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size.
- DNA fragments are negatively charged
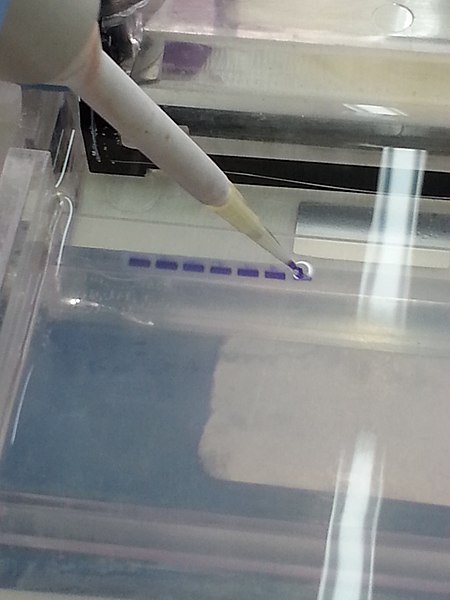
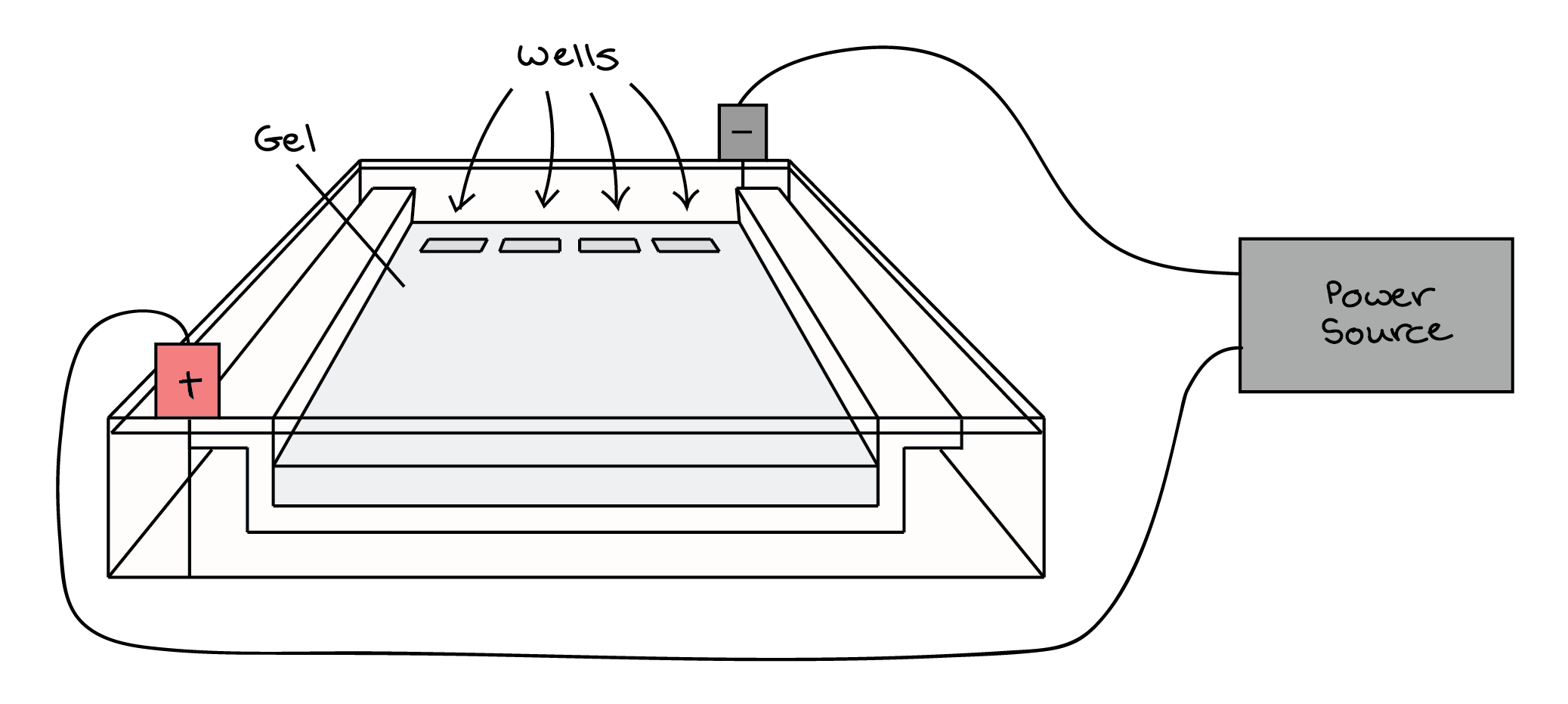
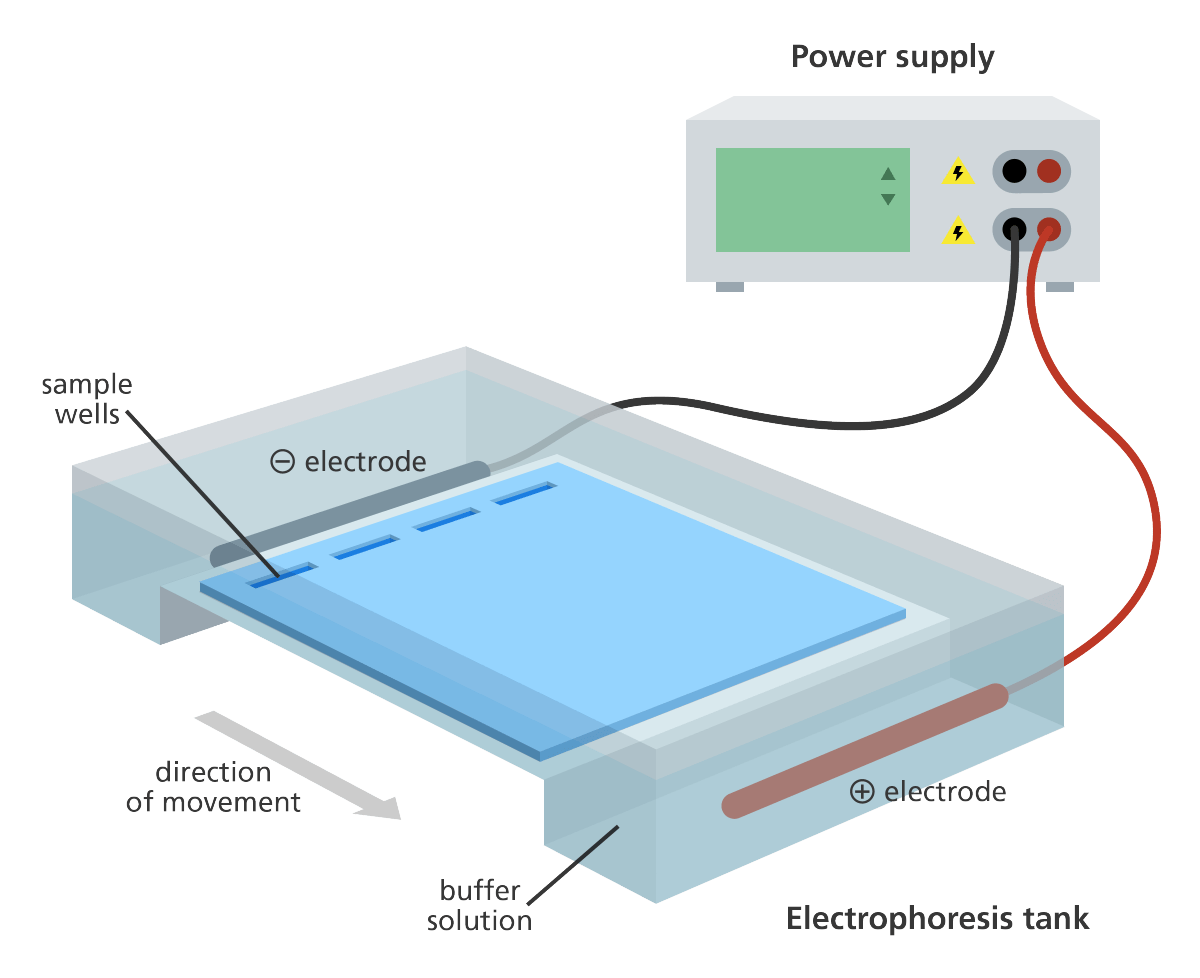
- DNA samples are loaded into wells (indentations) at one end of a gel, and an electric current is applied to pull them through the gel
- DNA fragments move towards the positive electrode
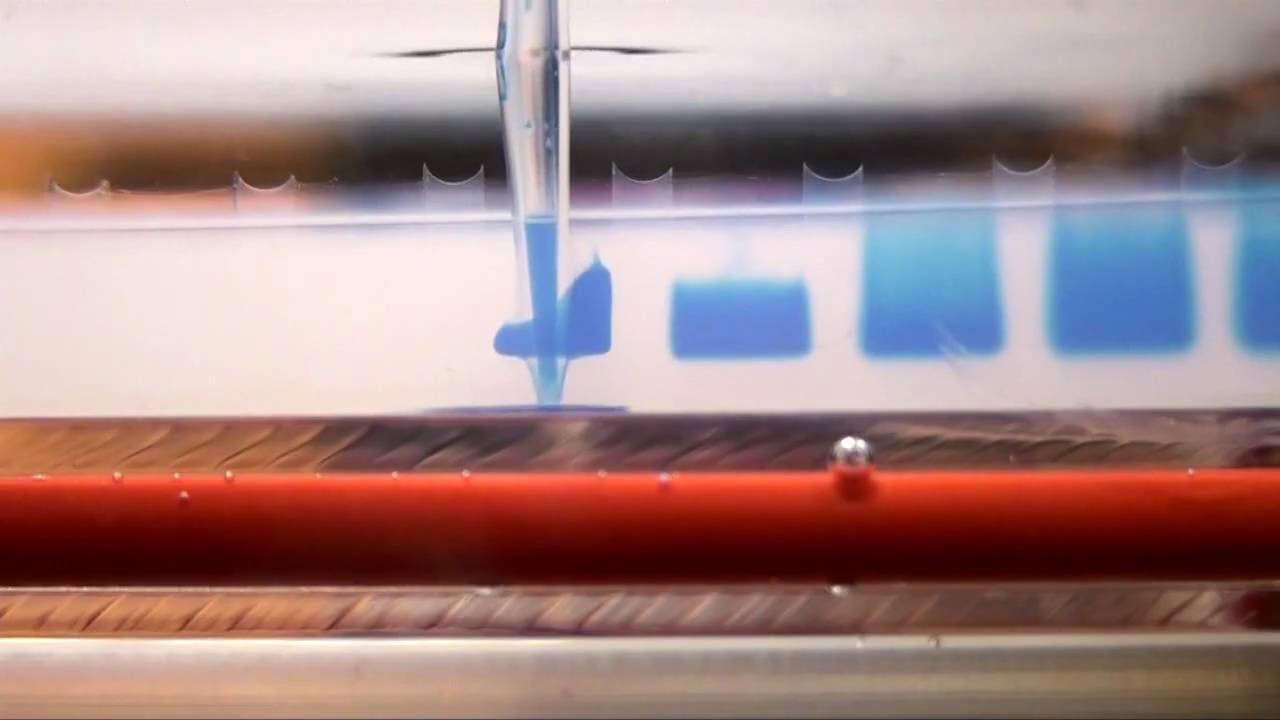
- Small fragments move through the gel faster than large ones.
- A gel is stained with a DNA-binding dye,
- the DNA fragments can be seen as bands, each representing a group of same-sized DNA fragments.
- PCR reaction vs DNA cloning
- Some DNA molecules are circular (like bacterial plasmids), while others are linear.
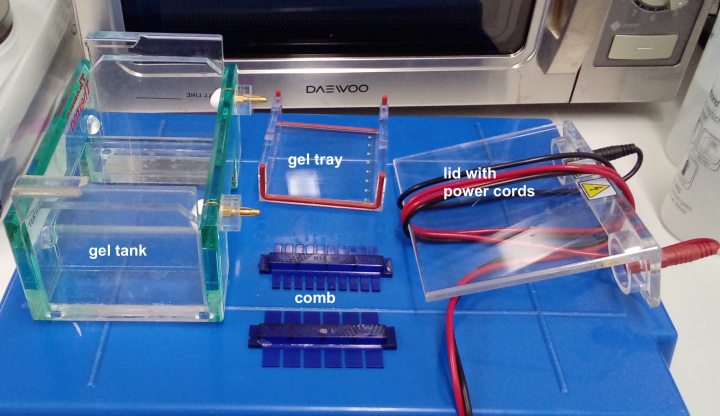
Materials
General Electrophresis Equipment:
Equipments
- Power Supply (voltage source)
- Gel Box (tank)
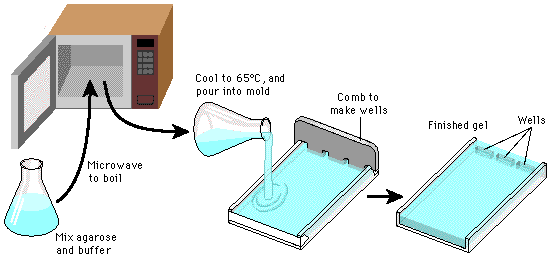
- Gel Mold
- Gel Form
- Gel tray (Casting tray)
- Lid with power cords
- Well combs
- UV light source
- Microwave
Reagents
- TAE
- Agarose
- Ethidum bromide (stock concentration of 10 mg/ml)
Experimental Procedure

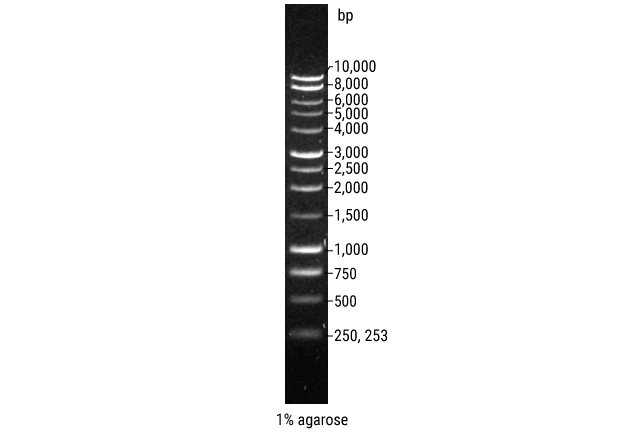
| Recommended % Agarose | Optimum Resolution for Linear DNA |
|---|---|
| 0.5 | 1,000–30,000bp |
| 0.7 | 800–12,000bp |
| 1.0 | 500–10,000bp |
| 1.2 | 400–7,000bp |
| 1.5 | 200–3,000bp |
| 2.0 | 50–2,000bp |
The greater the agarose concentration, the smaller the pores created in the gel matrix, and the more difficult it is for large linear DNA molecules to move through the matrix.
One liter 50X stock of TAE
- Tris-base: 242 g
- Acetate (100% acetic acid): 57.1 ml EDTA: 100 ml 0.5M sodium EDTA Add dH2O up to one litre.
- To make 1x TAE from 50X TAE stock, dilute 20ml of stock into 980 ml of DI water
- TBE can be used instead of TAE, labs usually use one or the other, but there is very little difference between the two.
- Note: Make sure to use the same buffer as the one in the gel box (do not mix different buffers and do not use water).

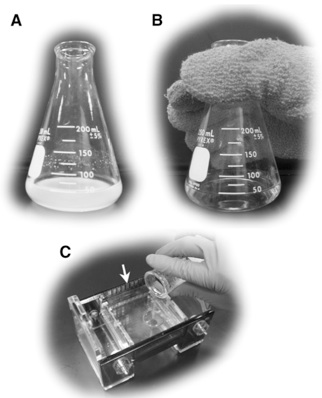
Very Hot! Cool Down







Flair: Science
Collection: Biology Crash Course
