Polymerase Chain Reaction
PCR Sample


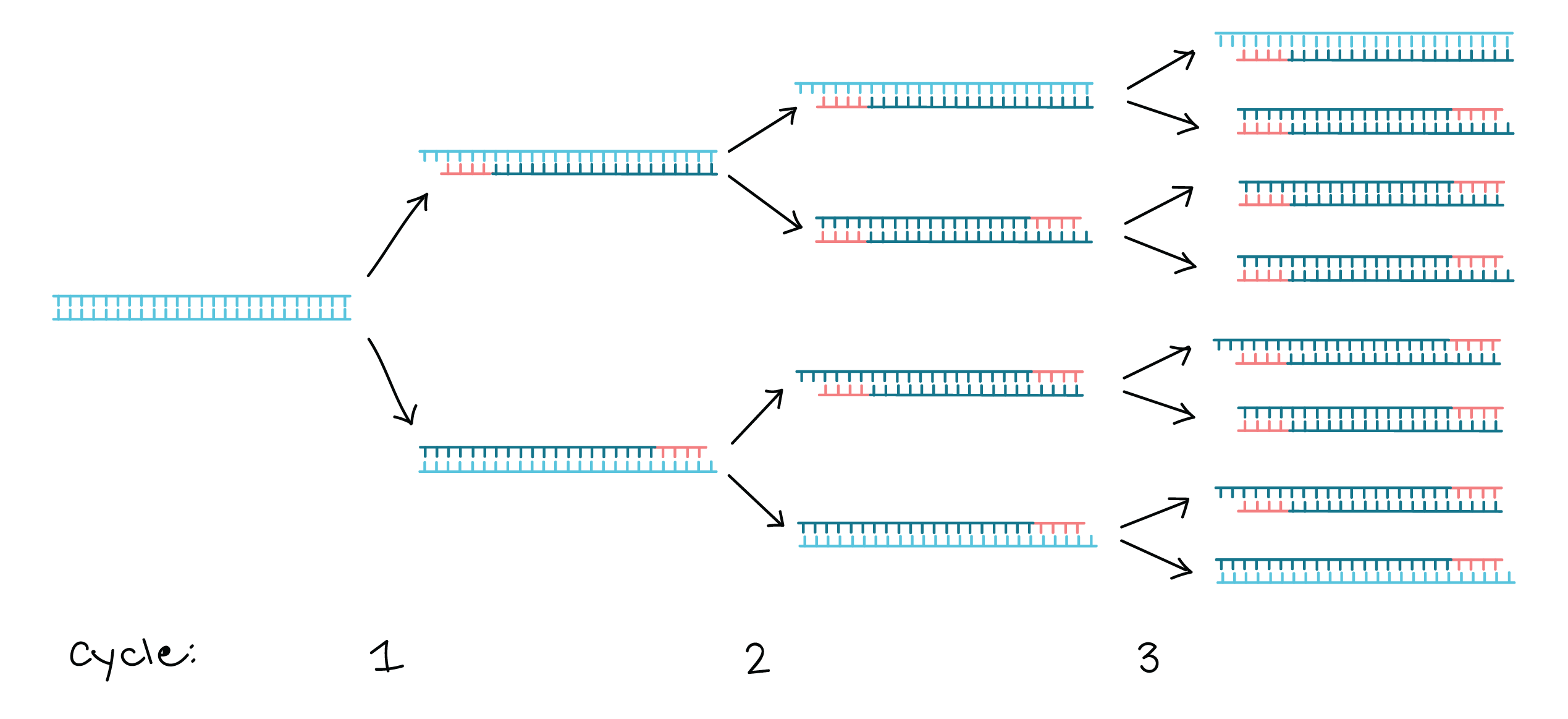
- Polymerase chain reaction, or PCR, is a technique to make many copies of a specific DNA region in vitro (in a test tube rather than an organism).
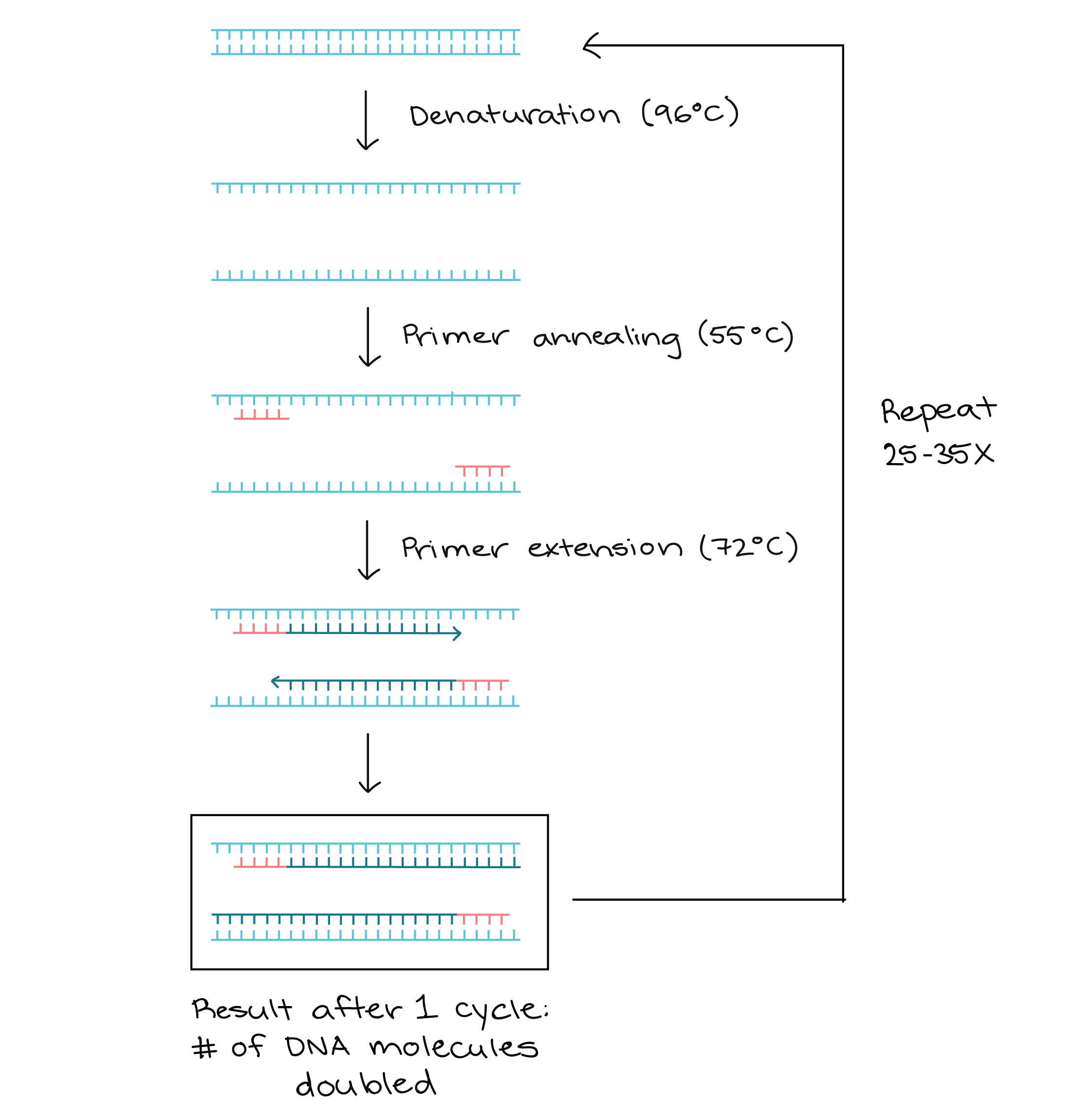
- PCR relies on a thermostable DNA polymerase, Taq polymerase, and requires DNA primers designed specifically for the DNA region of interest.
- In PCR, the reaction is repeatedly cycled through a series of temperature changes, which allow many copies of the target region to be produced.
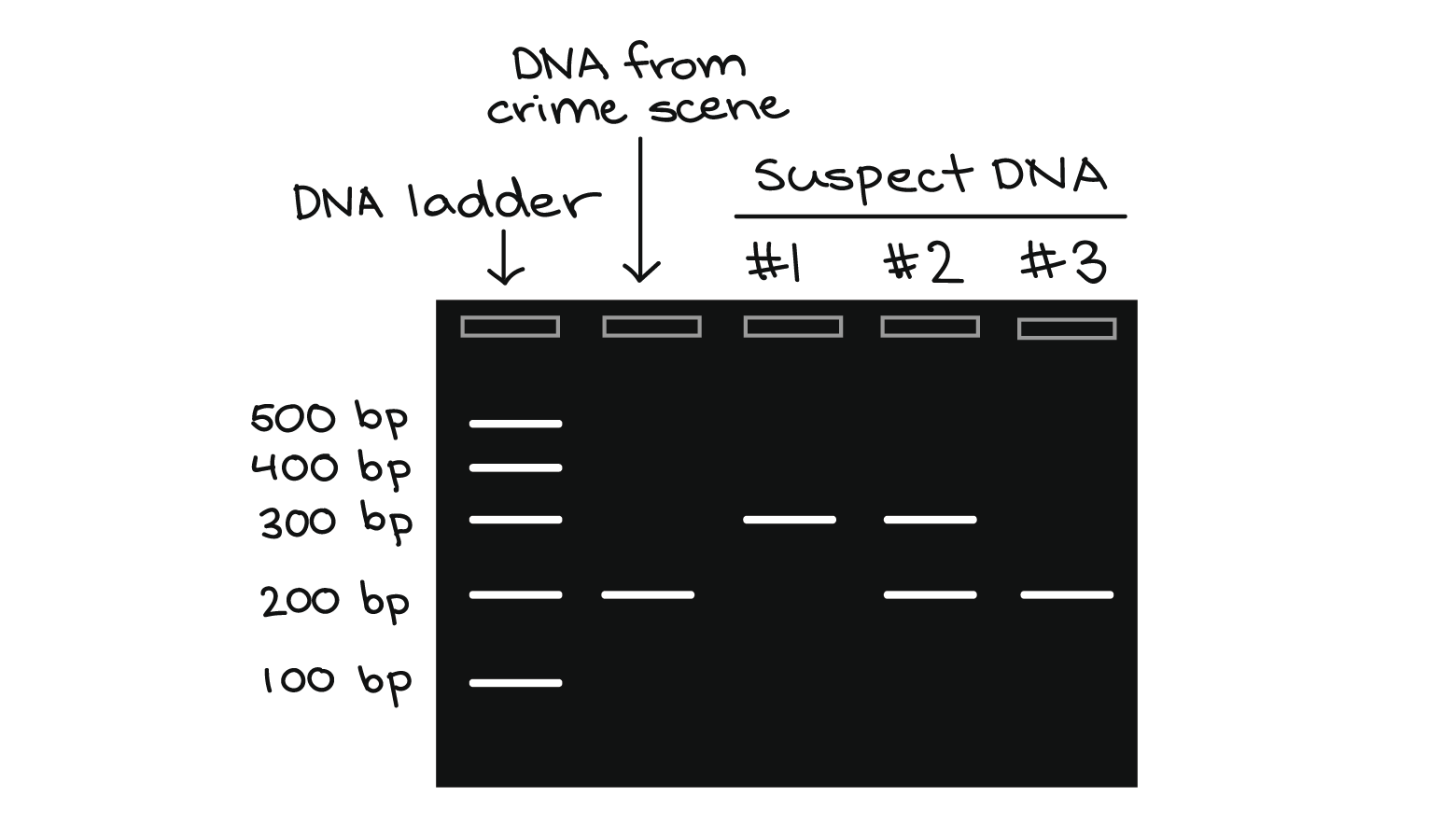
- PCR has many research and practical applications. It is routinely used in DNA cloning, medical diagnostics, and forensic analysis of DNA.
PCR is used in many research labs, and it also has practical applications in forensics, genetic testing, and diagnostics. For instance, PCR is used to amplify genes associated with genetic disorders from the DNA of patients (or from fetal DNA, in the case of prenatal testing). PCR can also be used to test for a bacterium or DNA virus in a patient's body: if the pathogen is present, it may be possible to amplify regions of its DNA from a blood or tissue sample.
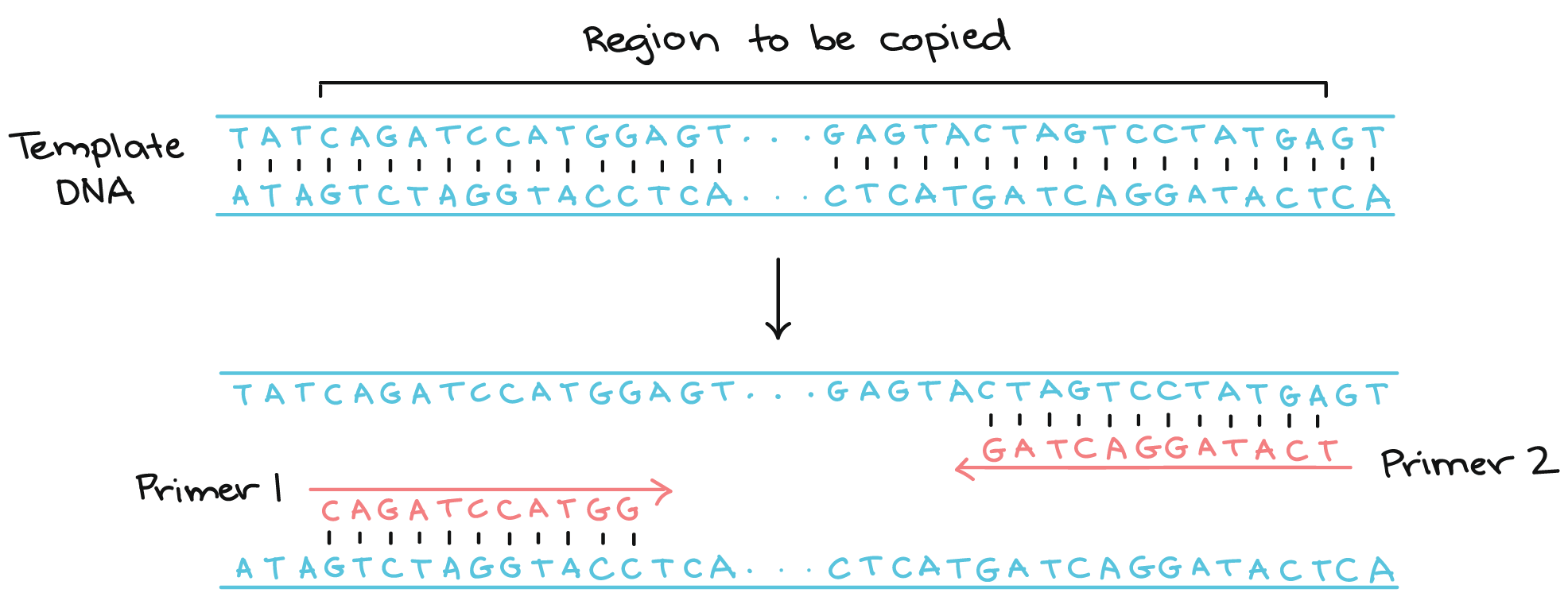
PCR primers are short pieces of single-stranded DNA, usually around 202020 nucleotides in length. Two primers are used in each PCR reaction, and they are designed so that they flank the target region (region that should be copied).

QIAquick PCR Purification Kit Protocol
using a microcentrifuge
This protocol is designed to purify single- or double-stranded DNA fragments from PCR and other enzymatic reactions (see page 8). For cleanup of other enzymatic reactions, follow the protocol as described for PCR samples or use the MinElute Reaction Cleanup Kit. Fragments ranging from 100 bp to 10 kb are purified from primers, nucleotides, polymerases, and salts using QIAquick spin columns in a microcentrifuge.
Important points before starting
- Add ethanol (96–100%) to Buffer PE before use (see bottle label for volume).
- All centrifugation steps are carried out at 17,900 x g (13,000 rpm) in a conventional tabletop microcentrifuge at room temperature.
- Add 1:250 volume pH indicator I to Buffer PB (i.e., add 120 µl pH indicator I to 30 ml Buffer PB or add 600 µl pH indicator I to 150 ml Buffer PB). The yellow color of Buffer PB with pH indicator I indicates a pH of #7.5.
- Add pH indicator I to entire buffer contents. Do not add pH indicator I to buffer aliquots.
- If the purified PCR product is to be used in sensitive microarray applications, it may be beneficial to use Buffer PB without the addition of pH indicator I.
Procedure
Add 5 volumes of Buffer PB to 1 volume of the PCR sample and mix. It is not necessary to remove mineral oil or kerosene.
For example, add 500 µl of Buffer PB to 100 µl PCR sample (not including oil).
If pH indicator I has beein added to Buffer PB, check that the color of the mixture is yellow.
If the color of the mixture is orange or violet, add 10 µl of 3 M sodium acetate, pH 5.0, and mix. The color of the mixture will turn to yellow.
Place a QIAquick spin column in a provided 2 ml collection tube.
To bind DNA, apply the sample to the QIAquick column and centrifuge for 30–60 s.
Discard flow-through. Place the QIAquick column back into the same tube.
Collection tubes are re-used to reduce plastic waste.
To wash, add 0.75 ml Buffer PE to the QIAquick column and centrifuge for 30–60 s.
Discard flow-through and place the QIAquick column back in the same tube. Centrifuge the column for an additional 1 min.
IMPORTANT: Residual ethanol from Buffer PE will not be completely removed unless the flow-through is discarded before this additional centrifugation.
Place QIAquick column in a clean 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube.
To elute DNA, add 50 µl Buffer EB (10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 8.5) or water (pH 7.0–8.5) to the center of the QIAquick membrane and centrifuge the column for 1 min. Alternatively, for increased DNA concentration, add 30 µl elution buffer to the center of the QIAquick membrane, let the column stand for 1 min, and then centrifuge.
IMPORTANT: Ensure that the elution buffer is dispensed directly onto the QIAquick membrane for complete elution of bound DNA. The average eluate volume is 48 µl from 50 µl elution buffer volume, and 28 µl from 30 µl elution buffer.
Elution efficiency is dependent on pH. The maximum elution efficiency is achieved between pH 7.0 and 8.5. When using water, make sure that the pH value is within this range, and store DNA at –20°C as DNA may degrade in the absence of a buffering agent. The purified DNA can also be eluted in TE buffer (10 mM Tris·Cl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0), but the EDTA may inhibit subsequent enzymatic reactions.
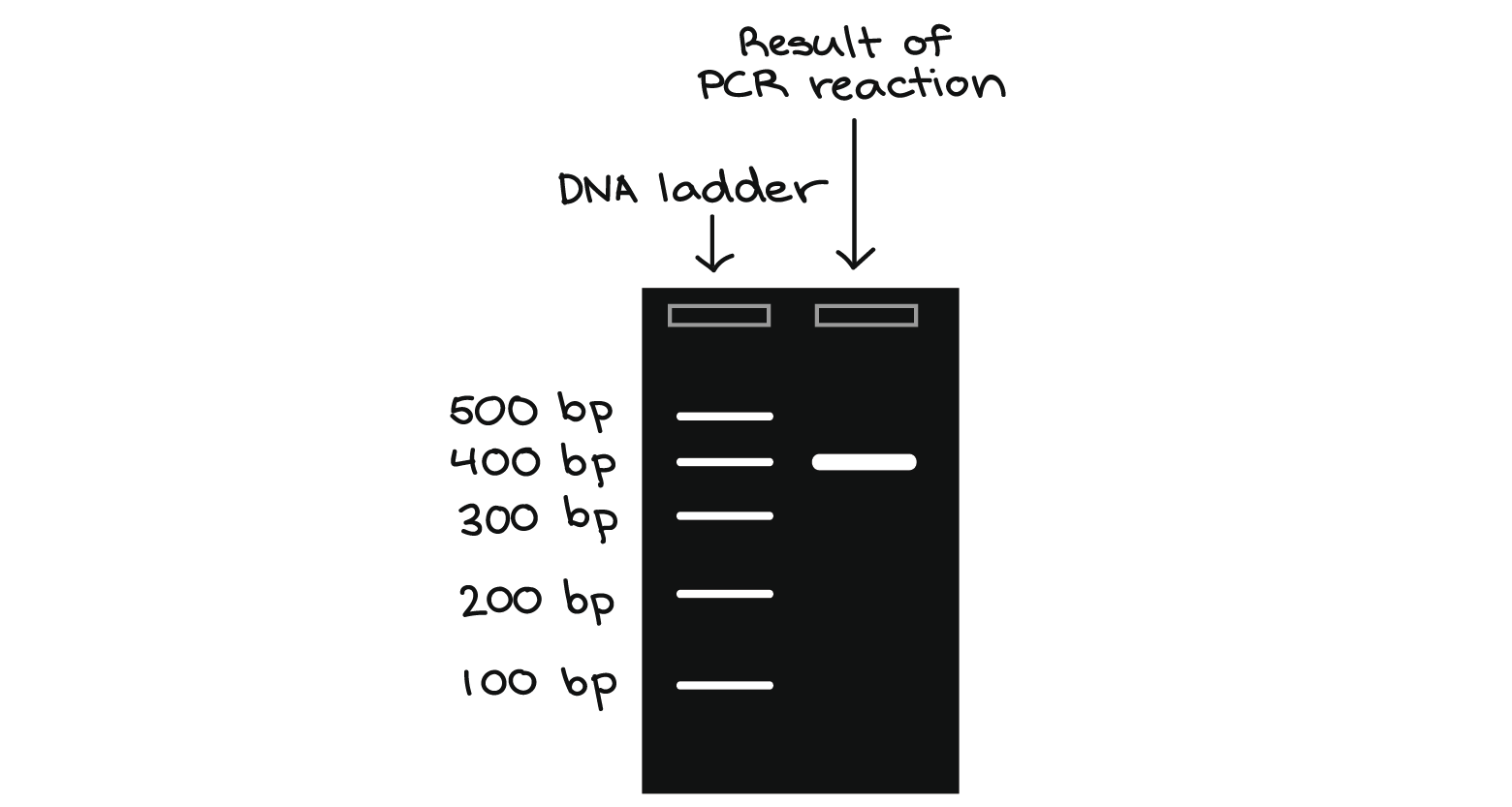
If the purified DNA is to be analyzed on a gel, add 1 volume of Loading Dye to 5 volumes of purified DNA. Mix the solution by pipetting up and down before loading the gel.
Loading dye contains 3 marker dyes (bromophenol blue, xylene cyanol, and orange G) that facilitate estimation of DNA migration distance and optimization of agarose gel run time. Refer to Table 2 (page 15) to identify the dyes according to migration distance and agarose gel percentage and type.
Sample problem
HIV detection in T-cells
Please write a lab report and use the lab protocol of DNA Electrophoresis.
Will submit
---

Flair: Science
Collection: Biology Crash Course
